Connectivity between nodes is established by either dynamic or proxy discovery.
dynamic discovery - all nodes in the cluster must be using the same discovery network address information and. The dynamic discover port is set in the node deployment configuration using the
NodeCommunication.discoveryPortconfiguration value (see the section called “Communication”) or at node installation (see the section called “Application installation” for details).Proxy discovery - nodes configure proxy node discovery for remote nodes in the node deployment configuration. Proxy nodes are configured in the
ProxyDiscovery.remoteNodes. See the section called “Communication” for details.
Connectivity between nodes can be verified on the
Discovered Nodes section of the High
Availability tab for a node (see Figure 6.1, “Distribution status”). For each remote node that has been
discovered this information is displayed:
Node Name - remote node name.
Network Address - network address used to connect to node.
Current State - current state of remote node.
Last State Change - the time of the last state change.
Number of Connections - current number of active TCP connections to the node.
Number of Queued PDUs - current number of protocol data units queued for this remote node when using asynchronous replication. This value is always 0 if synchronous replication is being used.
Discovered - how the node was discovered.
Location Code - internally generated location identifier for this node.
This information can also be displayed using:
epadmin --servicename=A.X display cluster --type=remote
A node has a single primary distribution listener address. However, there may be multiple distribution listener addresses associated with a node. The primary distribution listener address may change as engines are started and stopped. The primary listener address is used for all new connections from remote nodes.
The primary distribution listener address can be determined using
the display cluster
--type=local
// // Node A.X currently has two distribution listener addresses, // one on port 11838 associated with engine System::administration, // and one on port 11840 associated with engine application::Dtm_sbapp0 // The listener on port 11840 is the primary distribution listener. // epadmin --servicename=A.X display cluster --type=local [A.X] Node Name = A.X [A.X] Distribution State = Running [A.X] Active Distribution Listeners = System::administration:11838,application::Dtm_sbapp0:11840 [A.X] Number of Active Nodes = 1 [A.X] Number of Discovered Nodes = 1 [A.X] Number of Undiscovered Nodes = 0 [A.X] Number of Connections to Remote Nodes = 1 [A.X] Number of Type Mismatches = 0 [A.X] Location Code = 70263 [A.X] Primary Distribution Listener = IPv4:Kapoho.local:11840 // // Display remote nodes on remote node B.X. // Node B.X is connecting to port A.X using port 11840, // which as shown above is the current primary distribution listener // address for node A.X. // epadmin --servicename=B.X display cluster --type=remote [B.X] Node Name = A.X [B.X] Network Address = IPv4:Kapoho.local:11840 [B.X] Current State = Up [B.X] Last State Change = 2017-10-04 13:59:14 [B.X] Number of Connections = 5 [B.X] Number of Queued PDUs = 0 [B.X] Discovered = Dynamic [B.X] Location Code = 70263
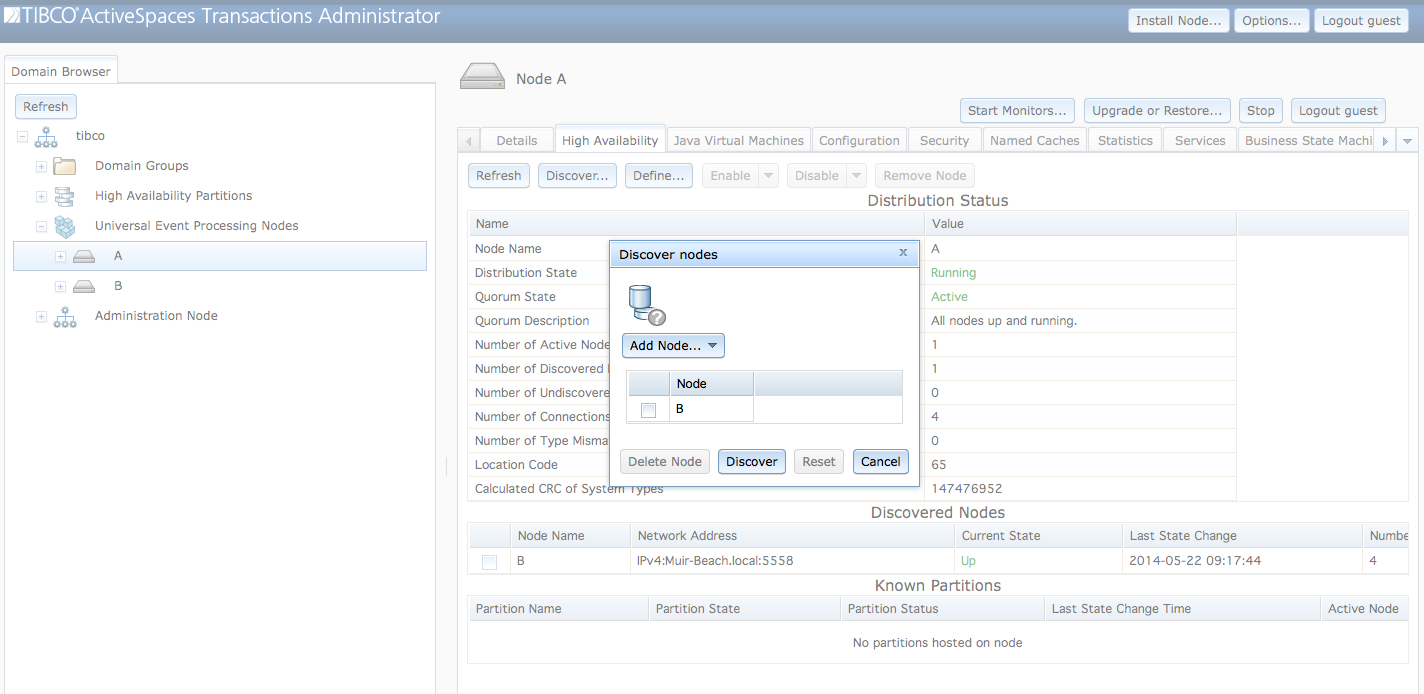
Operators can wait for distribution to attempt to discover
remote nodes using the Discover... button on the
High Availability tab as shown in Figure 6.3, “Discovering nodes”. Clicking on the
Discover button in the dialog attempts to establish
connectivity to the specified nodes.
Nodes can also be waited to be discovered using this command:
epadmin --servicename=A.X wait cluster --nodes=B,C
Discovered nodes in the Down state can be
removed by selecting a node in the Discovered Nodes
section and clicking on the Remove Node
button. This is useful when connectivity has been lost to a remote node,
or the node has been permanently removed from the cluster.
Nodes can also be removed using this command:
epadmin --servicename=A.X remove cluster --remotenode=B